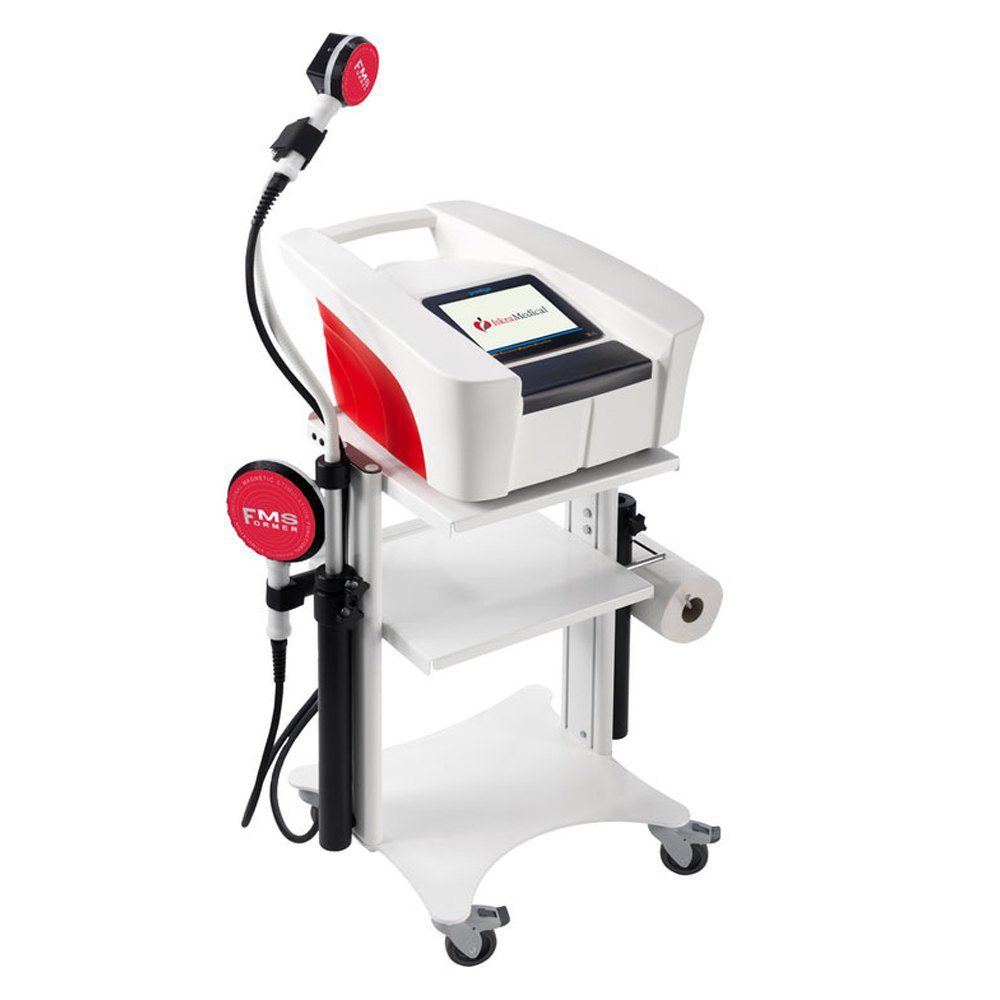

One of the initial applications of FMS was for the treatment of pelvic floor disorders, such as urinary incontinence. By targeting and stimulating the muscles of the pelvic floor, FMS aids in strengthening these muscles and restoring their normal function.
2. Deep Muscle Activation : FMS can penetrate and stimulate deeper muscles that are often hard to target with conventional electrical stimulation techniques. This is particularly beneficial for rehabilitation purposes and muscle strengthening.
3. Pain Management : Patients have reported relief from chronic pain conditions after undergoing FMS treatments. The magnetic fields can help in reducing muscle spasms and improving blood circulation, potentially aiding in pain relief.
4. Safe and Well-tolerated: Most patients experience minimal to no side effects. The most common sensations during treatment, such as mild discomfort or muscle twitching, are typically well-tolerated and diminish as the body becomes accustomed to the procedure.
BUDDHI CLINIC PRIVATE LIMITED © 2023 All rights reserved